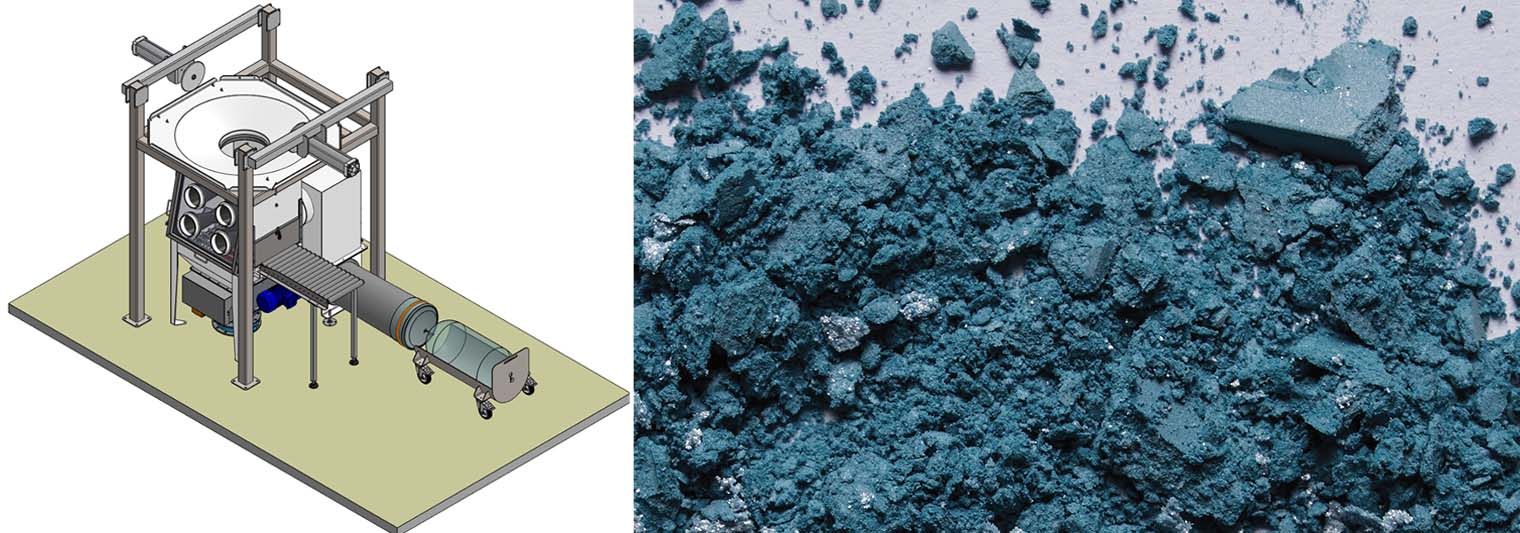
Les poudres de matières premières critiques (CRM) jouent un rôle essentiel dans la production de batteries, qui sont largement utilisées dans les véhicules électriques, les appareils électroniques portables et les systèmes de stockage d'énergie renouvelable.
Quels sont les types de poudres CRM utilisées dans la fabrication des batteries ?
Les principales poudres CRM utilisées dans la production de batteries lithium-ion sont :
Hydroxyde de lithium (LiOH)
L'hydroxyde de lithium est une matière première importante pour la production de cathodes pour les batteries lithium-ion. Il est utilisé pour fabriquer de l'oxyde de lithium nickel manganèse cobalt (NMC), de l'alumine lithium nickel cobalt (NCA) et d'autres composés cathodiques.
Oxyde de nickel (NiO)
L'oxyde de nickel est un composant clé des cathodes NMC et NCA, qui offrent une capacité énergétique élevée et une longue durée de vie. L'augmentation de la teneur en nickel dans les cathodes améliore la densité énergétique des batteries, ce qui est très important pour les applications automobiles.
Oxyde de cobalt (Co3O4)
L'oxyde de cobalt est utilisé dans la production de cathodes pour les batteries lithium-ion, en particulier dans les composés NMC et NCA. Bien que le cobalt soit un élément coûteux et controversé en raison des problèmes éthiques et environnementaux liés à son extraction, il contribue à améliorer la stabilité et les performances des batteries. Des efforts sont faits pour réduire la teneur en cobalt des cathodes ou pour développer des alternatives sans cobalt.
Oxyde de manganèse (MnO2)
L'oxyde de manganèse est utilisé dans la production de cathodes d'oxyde de lithium et de manganèse (LMO) et de cathodes NMC. Il offre une bonne stabilité thermique et une sécurité accrue pour les batteries lithium-ion, mais sa capacité énergétique est inférieure à celle des cathodes à base de nickel et de cobalt.
Les poudres de matières premières essentielles telles que l'hydroxyde de lithium, l'oxyde de nickel, l'oxyde de cobalt et l'oxyde de manganèse sont des composants clés dans la production des batteries lithium-ion et leur approvisionnement, leur traitement et leur utilisation ont un impact significatif sur les performances, le coût et la durabilité des batteries.
Ces composés sont utilisés dans la préparation des matériaux actifs de cathode (PCAM - Precursor Cathode Active Material), qui sont ensuite convertis en matériaux actifs de cathode(CAM - Cathode Active Material).

Do you need personal advice?
I am available to accompany you.
Loïc, powder expert
2. What are the physicochemical properties and associated dangers?
Critical Raw Materials (CRM) and toxic powders have several characteristics that make them potentially dangerous to human health and the environment, as well as to the safety of production processes.
Fine grain size
CRM powders often have a very fine particle size, making it easier for workers to inhale them and disperse them into the air. This can lead to respiratory problems, respiratory tract irritation and long-term health effects with prolonged exposure.
Chemical reactivity
Some CRM powders may react violently with water, air or other substances, releasing heat, toxic gases or other hazardous products. This reactivity can lead to risks for the safety of workers and facilities, as well as for the environment.
Toxicity
CRM powders may exhibit toxic effects on human health, even at low doses. Effects may vary depending on the nature and concentration of the substances, but may include skin irritation, respiratory problems, neurological effects or organ damage.
Flammability
Some CRM powders are flammable or present a risk of explosion under certain conditions, for example in the presence of ignition sources, airborne dust or high concentrations of flammable gases. This can pose risks to the safety of workers and facilities, as well as the environment.
Due to these hazardous characteristics, it is important to have appropriate protective measures in place, such as containment equipment, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment and safe handling procedures, to ensure worker safety , environmental protection and product quality when handling CRM powders.
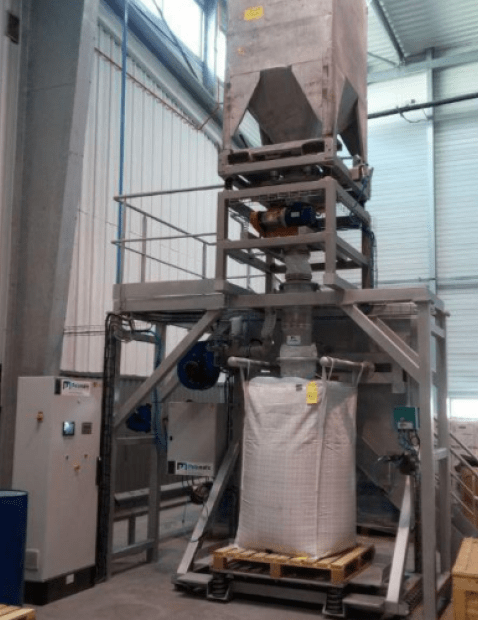
Big bag & sack discharging - Glove box - Duopal DP2

3. What are the health and environmental impacts of CRM and toxic powders?
Exposure to Critical Raw Materials (CRM) powders can have serious consequences on the health of workers and the environment.
Health effects may include:
Irritation of the respiratory tract and skin
Inhalation or skin contact with CRM powders may cause irritation, itching, redness and other unpleasant symptoms.
Allergic sensitization
Repeated exposure to CRM powders may lead to allergic sensitization, with allergic reactions such as asthma, rhinitis or eczema.
A potential carcinogenic effect
Some CRM powders, particularly those containing nickel and cobalt, may exhibit carcinogenic effects. Prolonged exposure or exposure to high concentrations may increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as lung or nasopharyngeal cancer.
Target organ toxicity
CRM powders may have toxic effects on specific organs, such as the liver, kidneys or nervous system. These effects can manifest as various symptoms, such as nausea, headache, dizziness or problems with memory and concentration.
Environmentally, CRM powders can have negative impacts such as:
Contamination of soil and water
CRM powders can settle on soils and enter ground or surface water, causing contamination and risks to aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
A disruption of ecosystems
Contamination by CRM powders can affect biodiversity and disrupt ecosystems, having toxic effects on plants, animals and microorganisms.
A long-term risk for biodiversity
The effects of CRM powder contamination can persist in the environment for long periods of time, with long-term consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
To minimize these risks to health and the environment, it is essential to put in place adequate protective measures, such as containment equipment, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment and safe handling procedures, when handling CRM powders.
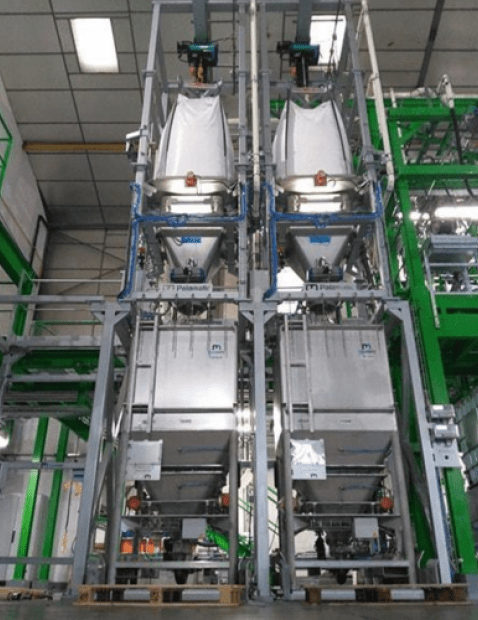
Case study: Big bag emptying and dosing for the manufacture of copper collectors for electric batteries