Cobots, or collaborative robots, are now a tangible reality transforming our factories. However, like any major technological shift, they bring both opportunities and challenges.
Unlike traditional robots, cobots are designed to work directly alongside humans. However, their integration into industrial processes presents both advantages and technical challenges.
This article provides a detailed analysis of the benefits of cobots, as well as the constraints to consider before implementing them.
1. Advantages of cobots in industry
Enhanced safety with cobots
Just like in Asimov’s works, cobots are designed to protect humans. Thanks to advanced sensors, they detect obstacles or workers nearby and adjust their movement or stop automatically to prevent accidents.
- Key technologies: Force sensors, 3D cameras, power-limiting systems.
- Concrete benefit: Reduced accident risk in shared work environments.
Flexibility and adaptability of cobots
Cobots can be programmed for a wide range of tasks, from material handling to quality control.
- Palletizing finished products
- Component assembly
- Handling delicate materials
Advantage: Reduced time and costs associated with production reconfiguration.
Improved productivity with cobots
By automating repetitive or strenuous tasks, cobots allow operators to focus on higher-value tasks. This efficiency gain recalls the technological utopia of The ice people.
- Impact: Continuous production and increased efficiency.
- Example: Using cobots for packaging ensures a consistent output rate.
Long-term cost reduction
Cobots require minimal modifications to existing infrastructures and consume less energy than traditional industrial robots.
- Maintenance cost: Low, thanks to standardized and durable components.
- Typical ROI: Often achieved within 1 to 3 years, depending on the application.
Improved working conditions
By handling the most physically demanding tasks, cobots reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and improve worker satisfaction.
Example: Handling heavy loads in a warehouse.
2. Disadvantages of cobots in industrial environments
Limited load capacity
Cobots are designed for light to moderate tasks. They are not suitable for applications requiring high power, high speed, or extreme precision.
- Payload capacity: Generally between 7 and 33 lbs.
- Limitation: Not suitable for heavy industries or extreme environments.
High initial cost
Although competitive compared to traditional industrial robots, cobots still represent a significant initial investment, particularly for small businesses.
- Typical cost: Between $20,000 and $50,000 CAD, excluding installation.
- Challenge: Justifying the investment for small production runs or short cycles.
Integration complexity
Integrating cobots into existing production lines may require extensive analysis and adjustments.
- Potential issues: Compatibility with existing equipment, software modifications.
- Solution: Plan a pilot testing phase before full-scale deployment.
Training requirements
Even though interfaces are intuitive, programming and managing cobots require initial training. Just like HAL 9000 in 2001: A space odyssey, a poorly controlled cobot can pose technical challenges.
- Time required: From a few hours to several days, depending on task complexity.
- Impact: Temporary productivity reduction during the transition phase.
Vulnerability to cyberattacks
Connected cobots can be a target for cyberattacks.
Requirement: Implement appropriate cybersecurity protocols.

Do you have a cobot implementation project?
I'm available to advise and support you in your study.
Guillaume, expert en cobot.
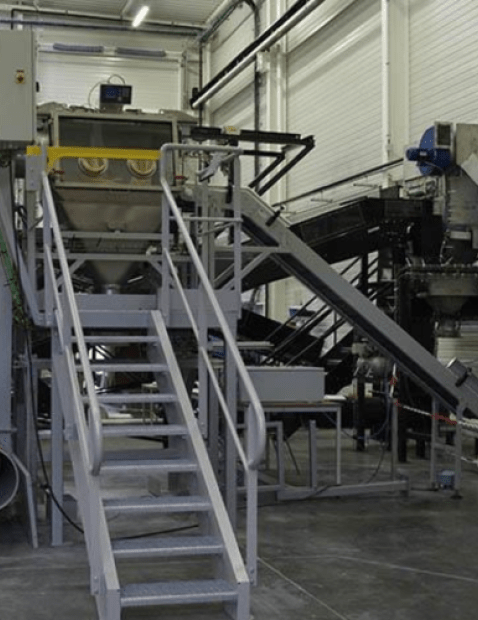
3. Examples of cobot applications at Palamatic Process
Handling of pouches
Context : Automating the loading and unloading of pouches.
Solution : Using cobots to handle various formats, adjust filling cycles, and ensure optimal throughput.
Outcome:
- Reduced worker fatigue
- 20% increase in productivity
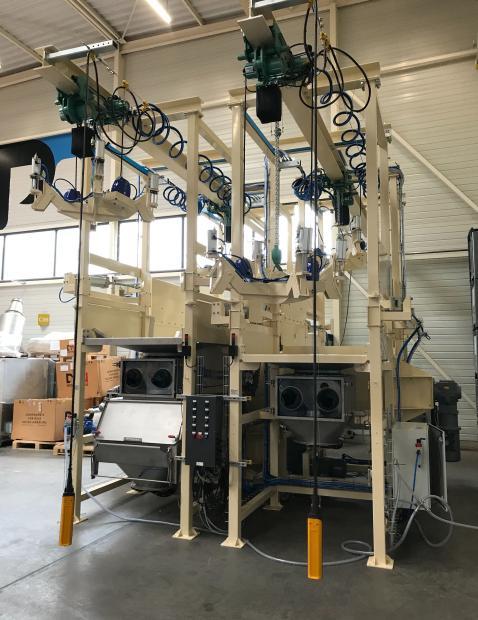
Automated packaging
Context : Packaging lines in the food industry.
Solution : Cobots integrated for assembly, screwing, and packaging.
Outcome :
- Increased production speed
- Reduced human errors
4. Comparison: Cobots vs. traditional industrial robots
| Criteria | Cobots | Traditional industrial robots |
|---|---|---|
| Human interaction | Direct collaboration | Isolated zones with barriers |
| Payload capacity | Up to 33 lbs | Several tons |
| Installation cost | Low (few modifications) | High (infrastructure required) |
| Maintenance | Easy and low-cost | Requires specialized servicing |
| Flexibility | Easy reprogramming | Limited to fixed tasks |
5. Recommendations for successful cobot adoption
- Assess needs: Identify repetitive, strenuous, or time-consuming tasks.
- Study feasibility: Analyze cobot compatibility with existing equipment and production workflows.
- Train teams: Schedule training sessions for quick onboarding.
- Plan integration: Conduct a pilot test before full-scale deployment.
- Ensure maintenance: Implement a monitoring program to optimize performance.
Useful links for further information
6. Les cobots, une solution technique stratégique
Cobots are powerful tools for modernizing industrial processes, but their adoption must be carefully planned. A rigorous analysis of needs, capabilities and constraints helps maximize their impact while minimizing technical obstacles.