- 1. What is a collaborative robot?
- 2. Differences between cobots and traditional robots
- 3. How cobots work and the technologies that make them unique
- 4. Why integrate cobots into your production lines?
- 5. Palamatic Process solutions integrating cobots
- 6. Industrial applications where cobots make a difference
- 7. The cost of cobots and their return on investment (ROI)
- 8. Future trends in industrial cobotics
Cobots, or collaborative robots, are a major advancement in the field of robotics. Unlike traditional industrial robots, these machines are designed to work closely with human operators without physical barriers.
Thanks to their built-in sensors and advanced safety systems, cobots ensure safe and productive interaction with their surroundings. This new approach to automation paves the way for more flexible, accessible, and efficient solutions tailored to the challenges of Industry 4.0.
What is a collaborative robot?
A collaborative robot, or cobot, is a type of industrial robot designed to work safely alongside humans without requiring physical separation, such as cages or barriers. Unlike traditional industrial robots, cobots integrate advanced safety and adaptability features, making them highly versatile and intuitive.
The origin and evolution of cobots
The concept of collaborative robotics emerged in the 1990s with the idea of complementing human skills rather than replacing them. This vision led to the development of robots capable of meeting diverse industrial needs while adhering to strict safety standards.
Companies like FANUC were pioneers in this field. Today, cobots are used in a wide range of industries, from automotive assembly lines to pharmaceutical laboratories and the food sector.
Differences between cobots and traditional robots
| Characteristics | Cobots | Traditional robots |
|---|---|---|
| Work environment | Share space with humans | Require secured zones (cages) |
| Installation | Simple, quick, and affordable | Complex and expensive |
| Programming | Accessible to non-expert operators | Automation expertise required |
| Flexibility | Adaptable to various tasks | Dedicated to fixed tasks |
| Safety | Advanced detection systems to avoid collisions | Limited or no collaborative features |
Example
On a production line, a traditional robot might exclusively handle packaging, while a cobot can manage packaging, quality control, and sorting assistance at the same station.

Do you have a cobot implementation project?
I'm available to advise and support you in your study.
Tarik, cobot expert.
How cobots work and the technologies that make them unique
Cobots stand out due to their advanced technological architecture, combining safety, flexibility, and performance.
Detection and safety systems
Cobots are equipped with sophisticated sensors such as 3D cameras, LIDAR and force sensors. These devices detect operators' movements and adjust their behavior in real time. For example, if a cobot detects a human presence too close, it automatically slows down or stops to avoid any risk of collision.
Intuitive cobot programming
Thanks to simplified user interfaces (often based on drag-and-drop), cobots can be programmed by non-specialist operators. This accessibility reduces integration costs and speeds up commissioning.
The mechanical flexibility of cobots
The articulated arms of cobots mimic human movements, enabling them to perform complex tasks with great precision.
Cobot communication and connectivity
Cobots are compatible with the main industrial protocols, such as OPC-UA, facilitating their integration into existing production lines.
Why integrate cobots into your production line?
Integrating cobots offers several strategic advantages:
- Reduced costs: Cobots are often less expensive than traditional robots, with limited maintenance needs.
- Enhanced safety: Built-in sensors reduce the risk of workplace accidents.
- Operational flexibility: Ideal for rapid production changes, cobots provide unmatched versatility.
- Increased productivity: By handling repetitive tasks, cobots free up time for operators to focus on higher-value activities.
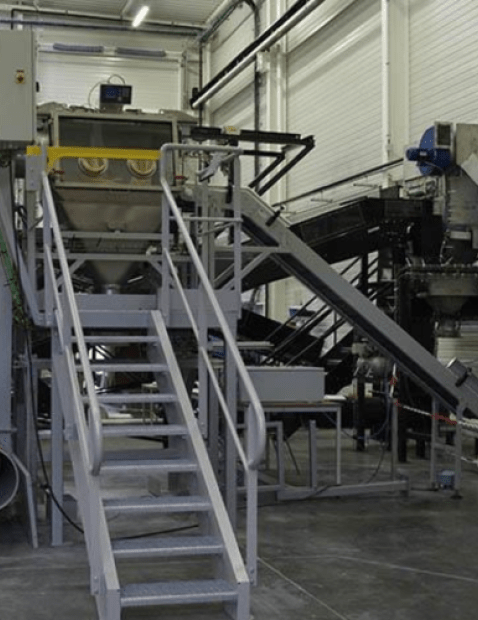
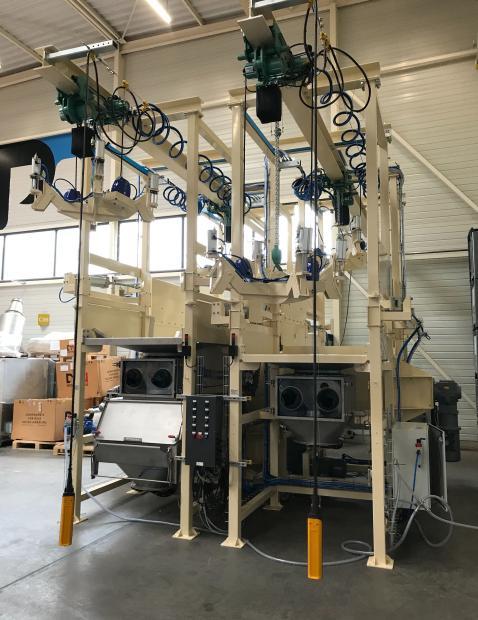
Palamatic Process solutions integrating cobots
Palamatic Process offers innovative solutions combining cobots with advanced industrial equipment:
- Powder decompaction: With SmashR® technology, cobots ensure safe and precise decompaction of materials before transfer.
- Automated filling: Flowmatic® stations guarantee fast, loss-free packaging.
- Toxic powder containment: Cobots collaborate with containment systems to minimize operator exposure risks.
Industrial applications where cobots make a difference
Thanks to their versatility and adaptability, cobots can be used in a wide range of industries.
Food industry
- Applications: Palletizing, packaging, delicate product handling.
- Example: Packing fruits or sweets without damaging them.
Pharmaceutical and chemical industries
- Applications: Precise dosing, handling in sterile containement, filling reactors.
- Example: Automated loading of toxic substances with operator protection.
Would you like to find out more? Read our case study on pharmaceutical packaging automation with cobots.
Logistics and automotive
- Applications: Small parts assembly, quality control.
- Example: Automated visuals inspection of components using 3D cameras.
The cost of cobots and their return on investment (ROI)
What is the cost of a cobot?
The price of a cobot generally varies between 20 000$ and 50 000$ USD, depending on the model and specific functionalities. This may seem a high price, but it's still lower than that of traditional robots, thanks in particular to reduced infrastructure requirements.
Return on investment (ROI)
Cobots offer an attractive ROI through:
- Lower installation costs: No need for physical barriers or heavy infrastructure.
- Increased productivity: By automating repetitive tasks, operators can focus on more valuable activities.
- Enhanced flexibility: Easily reconfigured for new tasks, cobots adapt to changing needs.
- Reduced labor costs: Cobots enable cost savings while maintaining consistent and efficient production.
Discover Palamatic Process' range of cobots and collaborative robots
Future trends in industrial cobotics
The future of cobots is promising, with innovations such as:
- Integrated AI: Cobots will continuously optimize their performance through autonomous learning.
- Expanded applications: Use in extreme environments (radioactive, underwater).
- Advanced materials: Built from lighter, more durable components, reducing their energy footprint.
For more information, visit the IFR (International Federation of Robotics) website.