- 1. Addressing geopolitical and economic challenges in strategic raw material sourcing.
- 2. Producing high-purity sulphates: a meticulous and rigorous process.
- 3. Mastering filtration and filter cake extraction to optimise production.
- 4. Converting sulphates into hydroxides: a key step for high-performance batteries.
- 5. Blending hydroxides for PCAM: ensuring uniformity for high-performance batteries.
- 6. From PCAM to CAM: the importance of thermal calcination.
An industrial revolution driven by innovation
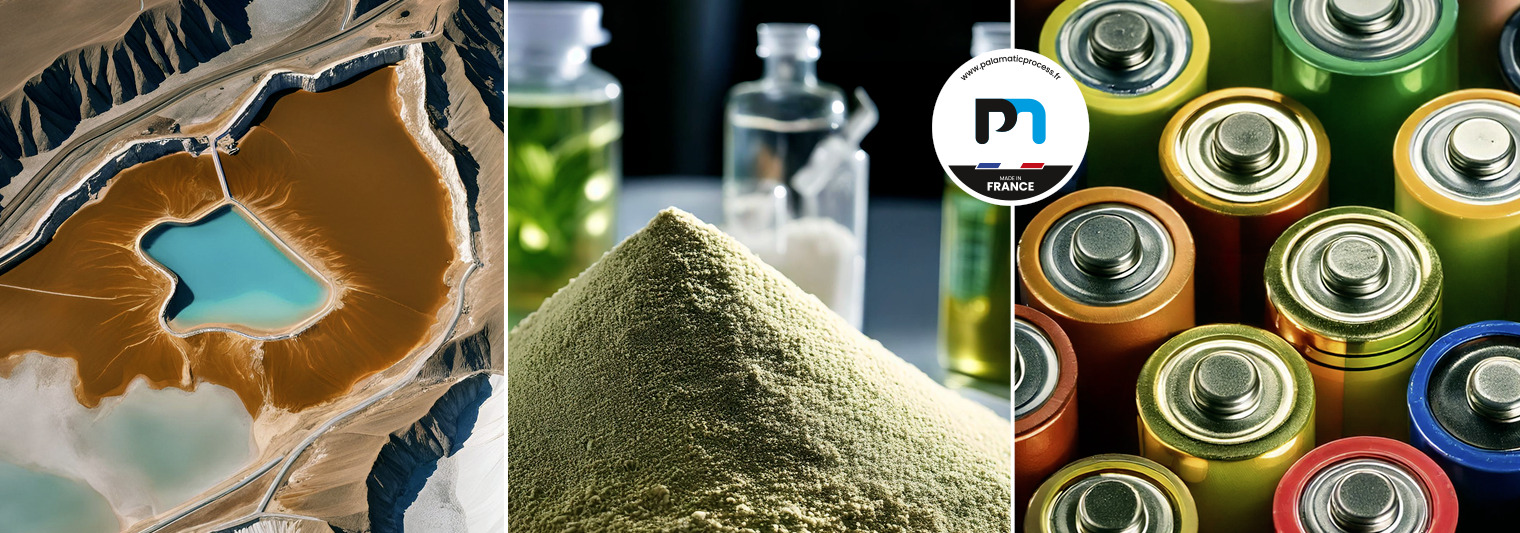
Lithium-ion batteries have become indispensable across a wide range of applications: electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and electronic devices. Their widespread use relies on a clever combination of cutting-edge technologies and highly optimised industrial processes.
Every step in their production — from raw material extraction to their final transformation into active materials for electrodes — is critical for ensuring the quality, performance, and durability of the batteries. These steps involve logistical, chemical, and technical challenges that demand advanced expertise.
Gigafactories are at the heart of this energy revolution. They orchestrate complex operations, starting with the strategic sourcing of raw materials. Collaborating with reliable suppliers ensures stable access to lithium, cobalt, manganese, and nickel — key elements in the production of lithium-ion batteries.
Addressing geopolitical and economic challenges in strategic raw material sourcing
The geopolitical and economic context
Sourcing raw materials for lithium-ion battery production is a complex task marked by significant geopolitical and economic challenges. Critical materials such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese are often concentrated in key strategic regions, making their extraction and supply particularly delicate.
Key materials and the role of major players
- Cobalt : The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) accounts for nearly 70% of global cobalt production. Political and social stability in the DRC is crucial for securing supplies.
- Lithium : Known as the "white gold" of the energy transiton, lithium is primarily extracted from South American salt flats (in Chile and Argentina) and Australian mines, which hold over three-quarters of the world's known reserves.
- Manganèse : South Africa and Gabon are key players, requiring close collaboration to ensure consistent supplies.
- Nickel : Indonesia, recently emerging as the global leader in nickel production, adds another layer of complexity to the supply chain.
Industrial strategies
Manufacturers adopt various strategies to address these challenges:
- Diversification of supply sources to reduce dependency on specific regions.
- Direct partnerships with producers to secure resources and mitigate geopolitical risks.
- Investment in recycling: Advanced recycling technologies reduce reliance on virgin resources and lower environmental impacts.

Do you work in the battery industry and have a powder handling project?
I'm available to discuss the subject with you.
Guillaume, powder expert
Producing high-purity sulphates: a meticulous and rigorous process
Once extracted, raw materials must be refined into intermediates such as nickel, cobalt, and manganese sulphates: essential precursors for electrode manufacturing.
The chemical process
In specialised reactors, ores are dissolved in sulphuric acid, often combined with oxidants to enhance reactivity. Temperature and pressure are meticulously controlled to maximise conversion efficiency.
Why purity matters
The sulphates’ purity, exceeding 99%, is vital to prevent parasitic reactions in subsequent steps. Impurities can degrade battery performance, reducing energy efficiency and lifespan.
Mastering filtration and filter cake extraction to optimise production
Filtration is a critical operation for separating solid impurities from the solution and recovering sulphates in the form of a homogeneous "filter cake."
Technologies in use
Advanced filter presses ensure rapid and effective separation, while hermetically sealed installations minimise contamination risks.
Advantages
A consistent "filter cake" streamlines transport and subsequent transformations while maintaining optimal quality and protecting workers from potential hazards.

Automated packaging process for filter cake in big bags with Palamatic Process
Converting sulphates into hydroxides: a key step for high-performance batteries
Sulphates are converted into hydroxides, such as nickel and manganese hydroxides, which are essential for producing active cathode materials.
Rigorous process
This reaction, using sodium hydroxide, requires precise control of parameters such as temperature, pH, and reactant concentrations to avoid impurities and ensure complete conversion.
Impact on batteries
The quality of hydroxides directly influences battery characteristics, including stability, capacity, and lifespan.
Blending hydroxides for PCAM: ensuring uniformity for high-performance batteries
The hydroxides are mixed to create PCAM (Precursors Cathode Active Material), the foundational material for positive electrodes.
Industrial process
Specialised equipment ensures uniform particle distribution and precise chemical composition to meet the stringent requirements of battery cells.
Results
High-quality PCAM ensures consistent charge distribution, minimising energy losses and enhancing chemical stability.

Automated preparation of CPTED with your Lithium, Nickel, Manganese and Cobalt hydroxides products
From PCAM to CAM: the importance of thermal calcination
The final step is calcination, where PCAM is exposed to temperatures of approximately 700°C to transform it into CAM (Cathode Active Material).
Effects of calcination
- Optimised crystallisation for enhanced electrochemical properties.
- Uniform integration of additives, such as lithium hydroxide, to stabilise cathodes.
Impact
High-quality CAM ensures greater energy density, extended lifespan, and improved cycle performance.
Conclusion
Lithium-ion battery production requires technical expertise at every stage, from sourcing raw materials to final calcination. Innovative solutions, such as those provided by Palamatic Process, help manufacturers meet performance and sustainability goals, supporting the energy transition.