Critical Raw Materials (CRM) powders play an essential role in the production of batteries, which are widely used in electric vehicles, portable electronics devices and renewable energy storage systems.
What types of CRM powders are used in battery manufacturing?
The main CRM powders used in the production of lithium-ion batteries are:
Lithium hydroxide (LiOH)
Lithium hydroxides is an important raw material for the production of cathodes for lithium-ion batteries. It is used to manufacture lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC), lithium nickel cobalt alumina (NCA) and other cathode compounds.
Nickel oxide (NiO)
Nickel oxide is a key component of NMC and NCA cathodes, offering high energy capacity and long life. Increasing nickel content in cathodes improves battery energy density, which is very important for automotive applications.
Cobalt oxide (Co3O4)
Cobalt oxide is used in the production of cathodes for lithium-ion batteries, particularly in NMC and NCA compounds. Although cobalt is a costly and controversial element due to the ethical and environmental problems associated with its extraction, it contributes to improving battery stability and performance. Efforts are being made to reduce the cobalt content of cathodes or to develop cobalt-free alternatives.
Manganese oxide (MnO2)
Manganese oxide is used in the production of lithium manganese oxide (LMO) cathodes and NMC cathodes. It offers good thermal stability and enhanced safety for lithium-ion batteries, but its energy capacity is lower that that of nickel- and cobalt-based cathodes.
Essential raw materials powders such as lithium hydroxide, nickel oxide, cobalt oxide and manganese oxide are key components in the production of lithium-ion batteries, and their sourcing, processing and use have a significant impact on battery performance, cost and durability.
These compounds are used in the preparation of cathode active materials (PCAM - Precursor Cathode Active Material), which are then converted into cathode active materials (CAM).

Do you have a powder-handling project?
I'm available to advise you and help determine the best solution.
Tarik, powder expert
2. What are the physico-chemical properties and associated hazards?
Critical Raw Materials (CRM) and toxic powders have a number of characteristics that make them potentially hazardous to human health and the environment, as well as to the safety of production processes.
Fine granulometry
CRM powders often have a very fine particle size, making them easy for workers to inhale and disperse in the air. This can lead to respiratory problems, respiratory tract irritation and long-term health effects in the event of prolonged exposure.
Chemical reactivity
Some CRM powders can react violently with water, air or other substances, releasing heat, toxic gases or other hazardous products. This reactivity may result in hazards to the safety of workers and installations, and to the environment.
Toxicity
CRM powders can have toxic effects on human health, even in small doses. Effects may vary according to the nature and concentration of the substances, but may include skin irritation, respiratory problems, neurological effects or organ damage.
Flammability
Some CRM powders are flammable or present an explosion hazard under certain conditions, for example in the presence of ignition sources, airborne dust or high concentrations of flammable gases. This can entail risks for the safety of workers and installations, as well as for the environment.
Because of these hazardous characteristics, it is important to put in place appropriate protective measures, such as containment equipment, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment and safe handling procedures, to ensure worker safety, environmental protection and product quality when handling CRM powders.
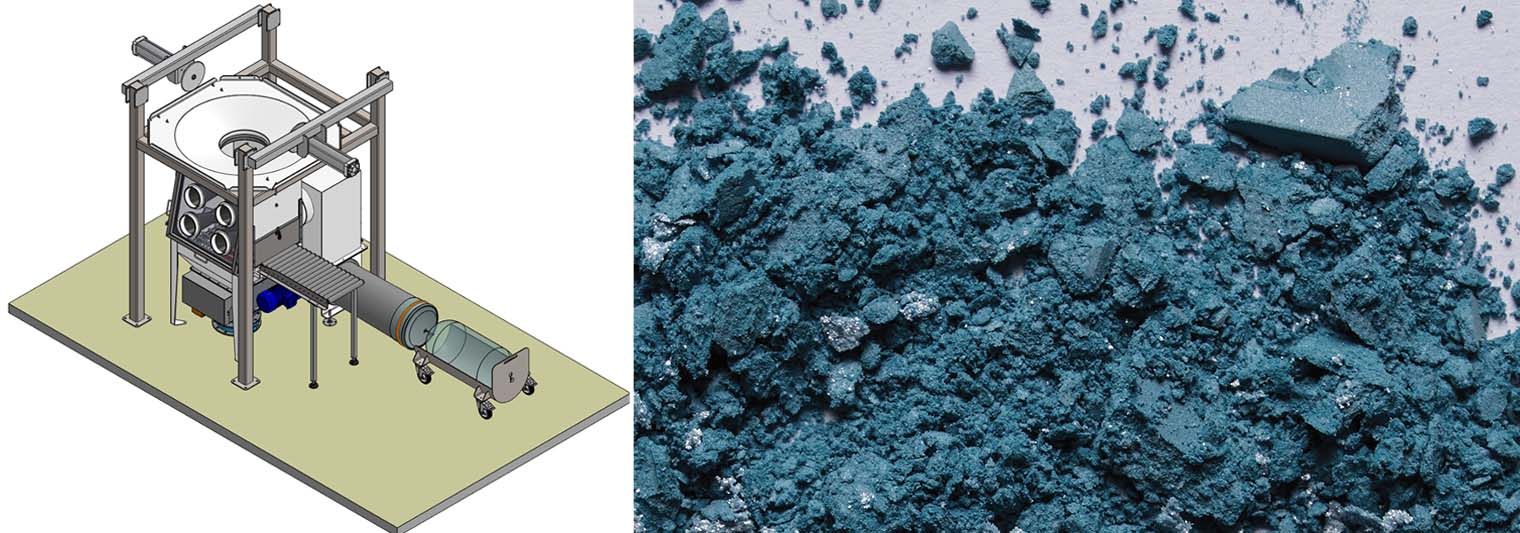
Big bag & sack discharging - Glove box - Duopal DP2

3. What are the health and environmental impacts of CRM and toxic powders?
Exposure to Critical Raw Materials (CRM) powders can have serious consequences for workers' health and the environment.
Health effects may include:
Irritation of the respiratory tract and skin
Inhalation or skin contact with CRM powders may cause irritation, itching, redness and other unpleasant symptoms.
Allergic sensitization
Repeated exposure to CRM powders may lead to allergic sensitization, with allergic reactions such as asthma, rhinitis or eczema.
Potential carcinogenic effect
Some CRM powders, particularly those containing nickel and cobalt, may be carcinogenic. Prolonged exposure or exposure to high concentrations may increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer, such as lung or nasopharyngeal cancer.
Target organ toxicity
CRM powders can have toxic effects on specific organs, such as the liver, kidneys or nervous system. These effects may manifest themselves in a variety of symptoms, such as nausea, headaches, dizziness, memory and concentration problems.
In environmental terms, CRM powders can have negative impacts such as:
Soil and water contamination
CRM powders can be deposited on soils and enter ground or surface water, leading to contamination and risks for aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Disruption of ecosystems
Contamination by CRM powders can affect biodiversity and disrupt ecosystems, with toxic effects on plants, animals and micro-organisms.
A long-term risk for biodiversity
The effects of CRM powder contamination can persist in the environment for long periods, with long-term consequences for biodiversity and ecosystem services.
To minimize these risks to health and the environment, it is vital to put in place adequate protective measures, such as containment equipment, ventilation systems, personal protective equipment and safe handling procedures, when handling CRM powders.
Case study: Big bag emptying and dosing for the manufacture of copper collectors for electric batteries